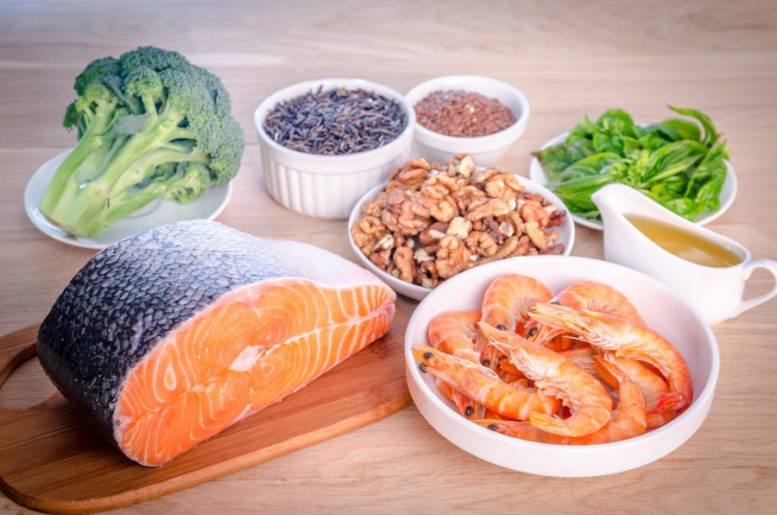
Omega- 3 fatty acids are essential fats. Although not produced by the human body, essential fats are required for your optimal health. Omega-3 helps to prevent cystic fibrosis, cognitive decline, rheumatoid arthritis, certain cancers, pulmonary hypertension, heart disease and strokes.
Researchers at Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health have identified three ways to include omega-3 in your nutritional plan:
- Eicosapentaenoic acid: (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) found mainly in fish, are sometimes referred to as marine omega-3s.
- Alphalinolenic acid (ALA), the most common omega-3 fatty acid in most Western diets, is found in vegetable oils, nuts (especially walnuts), flaxseeds and flax-seed oil, leafy vegetables, and animal fat (especially grass-fed animals). The human body generally uses ALA for energy and its conversion into EPA and DHA is very limited.
We need from 500 to 1,000 mg of omega-3 daily.
For optimal health and wellness, add these omega-3 rich foods to your diet:
Plant-Based Sources for Omega-3:
- Flaxseed
- Peanut butter
- Pumpkin seeds
- Walnuts
- Oatmeal
- Brussels sprouts
- Kale
- Mint
- Parsley
- Spinach
- Seaweed
Fish- Based Sources for Omega-3:
- Halibut
- Mackerel
- Salmon
- Tuna (fresh)
- Herring
- Oysters
Fortified Dairy and Juices with Omega-3:
- Eggs
- Soy milk
- Green super food juices
- Yogurt